
In today’s digital age, online security is of paramount importance. We go to great lengths to safeguard our personal and sensitive information, but sometimes, cyber threats can be lurking where we least expect them.

What Is DNS Spoofing?
It is stands for Domain Name System, and it is essentially the internet’s phone book. It translates human-friendly domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses (such as 192.168.1.1) that computers use to identify each other on the internet. DNS spoofing, also known as DNS cache poisoning, is a cyberattack where a malicious actor manipulates the DNS system to redirect traffic to a fraudulent website or server.
How Does DNS Spoofing Work?
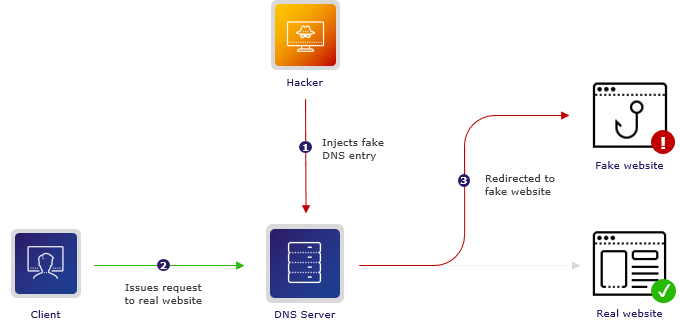
This spoofing occurs when an attacker manages to corrupt the DNS cache of a DNS server or a local device. Here’s a simplified version of how the attack unfolds:
- Request Intercept: When your device requests a website, it sends a DNS query to a DNS server, which then looks up the IP address associated with that domain.
- Manipulation: If an attacker intercepts this request, they can forge a response and send it back to your device before the legitimate its server does. This response can include a malicious IP address.
- Redirect: Your device, trusting the response it received, connects to the fraudulent IP address, which might lead to a fake website that mimics the legitimate one.
Why Is DNS Spoofing Dangerous?
This spoofing can lead to various security threats, including:
- Phishing Attacks: Attackers can redirect you to fake websites that look identical to legitimate ones, tricking you into revealing sensitive information like login credentials or financial details.
- Malware Distribution: DNS spoofing can be used to distribute malware by redirecting you to malicious download links or fake software updates.
- Data Theft: Attackers can intercept and steal sensitive data transmitted between you and a spoofed website.
Protecting Yourself from DNS Spoofing
Now that we understand the risks associated with DNS spoofing, here are some steps you can take to protect yourself:
- Use Trusted DNS Servers
- Enable DNSSEC
- Keep Software Updated
- Use a VPN
- Be Cautious
- Clear DNS Cache
Conclusion :
This spoofing is a stealthy cyberattack that can have serious consequences for your online security. By understanding how it works and taking proactive steps to protect yourself, you can minimize the risks associated with this type of attack. Stay vigilant, keep your software updated, and use trusted DNS servers to enjoy a safer online experience.